Convonet Sequence Diagram
Multi-LLM · LiveKit WebRTC · Domain Agents · Agent Monitor
Detailed Sequence Diagram
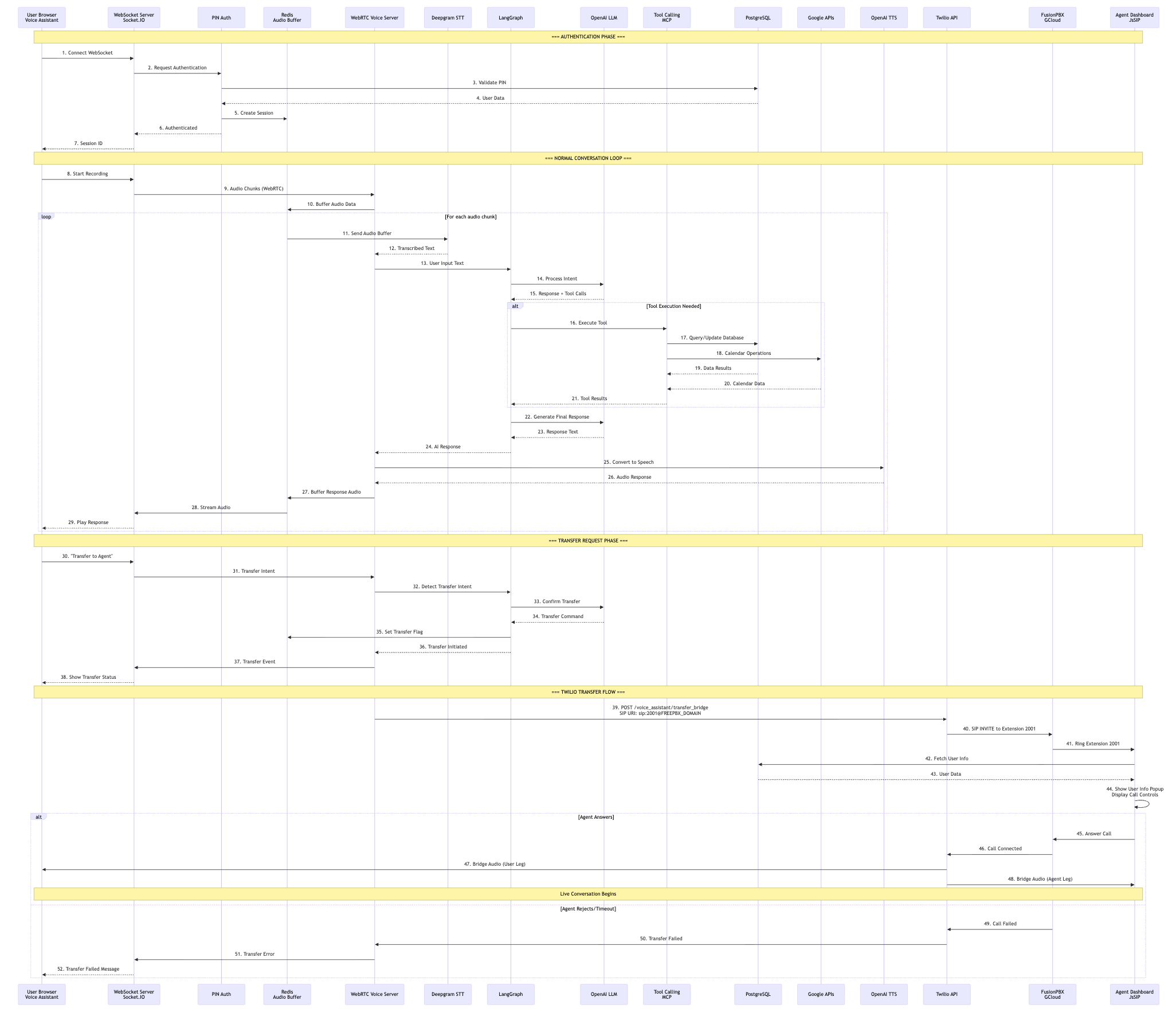
Sequence Phases
Phase 1: Authentication
Steps 1-7
Phase 2: Conversation Loop
Steps 8-31
Phase 3: Transfer Request
Steps 32-38
Phase 4: Twilio Transfer
Steps 39-52
Phase 1: Authentication (Steps 1-7)
User authentication and session creation
User Browser → WebSocket Server: Connect WebSocket
User opens the Convonet LiveKit WebRTC voice assistant UI and establishes a WebSocket connection via Socket.IO (or LiveKit) to the Flask server.
WebSocket Server → PIN Auth: Request Authentication
The WebSocket server requests PIN authentication from the authentication module.
PIN Auth → PostgreSQL: Validate PIN
PIN authentication module validates the user's PIN against PostgreSQL database using SQLAlchemy. Note: Authentication is handled via PostgreSQL, not FusionPBX.
PostgreSQL → PIN Auth: User Data
PostgreSQL returns user data including user ID, name, and team associations.
PIN Auth → Redis: Create Session
A new session is created in Redis with a unique session ID, storing user context and authentication status.
PIN Auth → WebSocket Server: Authenticated
Authentication module confirms successful authentication to the WebSocket server.
WebSocket Server → User Browser: Session ID
WebSocket server sends the session ID to the user browser. The user is now authenticated and ready to interact with the voice assistant.
Phase 2: Normal Conversation Loop (Steps 8-31)
Audio capture, transcription, AI processing, and response generation
User Browser → WebSocket Server: Start Recording
User initiates voice recording in the browser (LiveKit or MediaRecorder), beginning the audio capture process.
WebSocket Server → LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server: Audio Chunks
Audio chunks are streamed from the browser via LiveKit WebRTC (or Socket.IO) to the LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server (webrtc_voice_server_socketio.py).
LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server → Redis: Buffer Audio Data
Each session's audio chunks are appended to a Redis buffer (convonet.redis_manager) so downstream workers can read them for processing.
Redis → Deepgram STT: Send Audio Buffer → Transcribed Text
The voice server reads the buffer and forwards it to streaming Deepgram STT for transcription. Deepgram returns the recognized text back to the voice service.
Important: Deepgram STT is used for voice audio, not Twilio transcription.
LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server → LangGraph → Multi-LLM: Process Intent
The transcript enters the LangGraph assistant. LangGraph calls the selected LLM (Claude, Gemini, or OpenAI) for reasoning and response generation. Domain agents (Productivity, Mortgage, Healthcare) may be invoked. Agent Monitor tracks the interaction. LLM returns response and tool calls to LangGraph.
Tool Execution (If Needed)
If the LLM decides to execute an action, LangGraph invokes registered MCP tools. Agent Monitor records each tool call with elapsed time.
- Database Operations: PostgreSQL queries/updates via SQLAlchemy
- Calendar Operations: Google Calendar/OAuth workflows
- PBX Metadata: FusionPBX lookups for call metadata
Tool results are injected back into the LangGraph state, and the LLM composes the final reply.
LangGraph → Multi-LLM → LangGraph: Generate Final Response
LangGraph sends context to the selected LLM (Claude, Gemini, or OpenAI) for final response generation. LLM returns response text to LangGraph, which passes it to the LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server.
Streaming TTS → Redis → WebSocket → User: Audio Response
Final text is synthesized via streaming TTS (Deepgram, ElevenLabs, or Cartesia). The audio response is streamed back over Socket.IO/LiveKit to the browser for playback. Audio may be buffered in Redis for smooth playback.
Phase 3: Transfer Request (Steps 32-38)
User requests transfer and system initiates transfer process
User Browser → WebSocket Server: "Transfer to Agent"
User says "I need a human" or requests transfer to a human agent.
WebSocket Server → LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server → LangGraph: Transfer Intent
Transfer intent is passed through the LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server to LangGraph for detection and processing.
LangGraph → Multi-LLM: Detect Transfer Intent → Transfer Command
LangGraph detects transfer intent and confirms with the selected LLM. LLM returns a transfer command to LangGraph.
LangGraph → Redis: Set Transfer Flag
LangGraph sets a transfer flag in Redis to indicate that a transfer is in progress.
LangGraph → LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server → WebSocket Server → User: Transfer Initiated
Transfer initiated signal flows back through the system. LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server sends transfer event to WebSocket Server, which notifies the user browser. User sees transfer status update.
Phase 4: Twilio Transfer Flow (Steps 39-52)
Call bridging to FusionPBX and agent dashboard connection
LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server → Twilio API: POST /voice_assistant/transfer_bridge
The voice backend calls the Convonet /twilio/voice_assistant/transfer_bridge endpoint. Twilio uses the provided SIP URI: sip:2001@FREEPBX_DOMAIN;transport=udp or trunk number, depending on .env configuration.
Twilio → FusionPBX: SIP INVITE to Extension 2001
Twilio dials FusionPBX (running on Google Cloud) via SIP INVITE. FusionPBX routes the call to the target agent extension (e.g., 2001).
FusionPBX → Agent Dashboard: Ring Extension 2001
FusionPBX rings extension 2001. The agent dashboard (JsSIP client) registers with FusionPBX over WSS (wss://<fusionpbx>:7443) and receives the incoming call notification.
Agent Dashboard → PostgreSQL: Fetch User Info → Show User Info Popup
Agent dashboard fetches caller record from PostgreSQL via REST API. Dashboard pops the caller record and shows ringing controls with user information (name, context, call history).
Agent Answers → Conversation Begins
Agent answers the call via JsSIP client. FusionPBX notifies Twilio that the call is connected. Twilio bridges the audio between user leg and agent leg. Live conversation begins between the user and agent.
Note: Once Twilio bridges the call to FusionPBX, the audio is now a PSTN/SIP leg (not the original WebRTC stream). Deepgram STT may still be used on the server side for context logging if needed.
Alternative: Agent Rejects/Timeout
If the agent rejects the call or it times out:
- FusionPBX notifies Twilio that the call failed
- Twilio sends transfer failed notification to LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server
- LiveKit WebRTC Voice Server sends transfer error event to WebSocket Server
- User browser displays transfer failed message
Key Sequence Points
Authentication Path
PIN authentication uses PostgreSQL (not FusionPBX). Sessions are stored in Redis for fast access.
Audio Processing
Streaming Deepgram STT for voice transcription. TTS via Deepgram, ElevenLabs, or Cartesia. Redis buffers audio chunks when needed.
AI Orchestration
LangGraph coordinates between Multi-LLM (Claude, Gemini, OpenAI), domain agents, and MCP tools. Agent Monitor tracks tool calls and voice timing.
Transfer Mechanism
Twilio bridges the LiveKit WebRTC user leg to the SIP agent leg. Audio transitions from WebRTC to PSTN/SIP stream.
Agent Monitor
Real-time observability at /agent-monitor/. Tracks tool calls with elapsed time and voice timing (buffer capture, STT, agent start, first sentence, first audio).